The Essential Guide to Requirements Management and Traceability
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Fundamentals of Requirements Management
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 What is Traceability?
- 2 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 3 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 4 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 5 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 6 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 7 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 8 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 9 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 10 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 11 How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability
- 12 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 13 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 14 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 15 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- Glossary
Chapter 4: Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
Chapters
- 1. Requirements Management
- Overview
- 1 What is Requirements Management?
- 2 Why do you need Requirements Management?
- 3 Four Fundamentals of Requirements Management
- 4 Adopting an Agile Approach to Requirements Management
- 5 Status Request Changes
- 6 Conquering the 5 Biggest Challenges of Requirements Management
- 7 Three Reasons You Need a Requirements Management Solution
- 2. Writing Requirements
- Overview
- 1 Functional requirements examples and templates
- 2 Identifying and Measuring Requirements Quality
- 3 How to write system requirement specification (SRS) documents
- 4 The Fundamentals of Business Requirements: Examples of Business Requirements and the Importance of Excellence
- 5 Adopting the EARS Notation to Improve Requirements Engineering
- 6 Jama Connect Advisor™
- 7 Frequently Asked Questions about the EARS Notation and Jama Connect Advisor™
- 8 How to Write an Effective Product Requirements Document (PRD)
- 9 Functional vs. Non-Functional Requirements
- 10 What Are Nonfunctional Requirements and How Do They Impact Product Development?
- 11 Characteristics of Effective Software Requirements and Software Requirements Specifications (SRS)
- 12 8 Do’s and Don’ts for Writing Requirements
- 3. Requirements Gathering and Management Processes
- Overview
- 1 Requirements Engineering
- 2 Requirements Analysis
- 3 A Guide to Requirements Elicitation for Product Teams
- 4 Requirements Gathering Techniques for Agile Product Teams
- 5 What is Requirements Gathering?
- 6 Defining and Implementing a Requirements Baseline
- 7 Managing Project Scope — Why It Matters and Best Practices
- 8 How Long Do Requirements Take?
- 4. Requirements Traceability
- Overview
- 1 What is Traceability?
- 2 Tracing Your Way to Success: The Crucial Role of Traceability in Modern Product and Systems Development
- 3 Change Impact Analysis (CIA): A Short Guide for Effective Implementation
- 4 What is Requirements Traceability and Why Does It Matter for Product Teams?
- 5 Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
- 6 Unraveling the Digital Thread: Enhancing Connectivity and Efficiency
- 7 The Role of a Data Thread in Product and Software Development
- 8 How to Create and Use a Requirements Traceability Matrix
- 9 Traceability Matrix 101: Why It’s Not the Ultimate Solution for Managing Requirements
- 10 Live Traceability vs. After-the-Fact Traceability
- 11 How to Overcome Organizational Barriers to Live Requirements Traceability
- 12 Requirements Traceability, What Are You Missing?
- 13 Four Best Practices for Requirements Traceability
- 14 Requirements Traceability: Links in the Chain
- 15 What Are the Benefits of End-to-End Traceability During Product Development?
- 5. Requirements Management Tools and Software
- Overview
- 1 Selecting the Right Requirements Management Tools and Software
- 2 Why Investing in Requirements Management Software Makes Business Sense During an Economic Downturn
- 3 Why Word and Excel Alone is Not Enough for Product, Software, and Systems Development
- 4 Application lifecycle management (ALM)
- 5 Is There Life After DOORS®?
- 6 Checklist: Selecting a Requirements Management Tool
- 6. Requirements Validation and Verification
- 7. Meeting Regulatory Compliance and Industry Standards
- Overview
- 1 Understanding ISO Standards
- 2 Understanding ISO/IEC 27001: A Guide to Information Security Management
- 3 What is DevSecOps? A Guide to Building Secure Software
- 4 Compliance Management
- 5 What is FMEA? Failure Modes and Effects Analysis
- 6 TÜV SÜD: Ensuring Safety, Quality, and Sustainability Worldwide
- 8. Systems Engineering
- 9. Automotive Development
- 10. Medical Device & Life Sciences Development
- Overview
- 1 The Importance of Benefit-Risk Analysis in Medical Device Development
- 2 Software as a Medical Device: Revolutionizing Healthcare
- 3 What’s a Design History File, and How Are DHFs Used by Product Teams?
- 4 Navigating the Risks of Software of Unknown Pedigree (SOUP) in the Medical Device & Life Sciences Industry
- 5 What is ISO 13485? Your Comprehensive Guide to Compliant Medical Device Manufacturing
- 6 What You Need to Know: ANSI/AAMI SW96:2023 — Medical Device Security
- 7 ISO 13485 vs ISO 9001: Understanding the Differences and Synergies
- 8 Failure Modes, Effects, and Diagnostic Analysis (FMEDA) for Medical Devices: What You Need to Know
- 9 Embracing the Future of Healthcare: Exploring the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
- 11. Aerospace & Defense Development
- 12. Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC industry) Development
- 13. Industrial Manufacturing & Machinery, Automation & Robotics, Consumer Electronics, and Energy
- Glossary
Key Traceability Challenges and Tips for Ensuring Accountability and Efficiency
In today’s rapidly evolving world, traceability has become a crucial aspect of various industries. From medical devices and pharmaceuticals to electronics and automotive, traceability plays a pivotal role in improving quality control, and adhering to regulatory compliance. However, despite its significance, businesses often encounter numerous challenges when implementing effective traceability systems.
In this subchapter, we’ll explore some three key traceability challenges faced by organizations, why it is so vital in the modern development landscape, and what you can do to improve your traceability practices. But first, let’s set the stage as to what requirements traceability is and why it’s so important.
Why is Traceability Important?
Traceability serves as a fundamental building block for several critical aspects of modern business operations. Here are some key reasons why traceability is of paramount importance:
- Quality Control and Risk Mitigation: Traceability empowers businesses to identify the source of defects or issues in their products or processes quickly. By pinpointing the root cause, organizations can take corrective actions promptly, reducing the risk of widespread problems and enhancing overall product, systems, and software quality.
- Consumer Safety and Trust: In industries like medical devices and pharmaceuticals, traceability ensures that any potential hazards or recalls can be contained efficiently, safeguarding consumer safety. This transparency fosters trust and loyalty among customers, positively impacting a company’s reputation.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meeting regulatory standards is non-negotiable for businesses offering complex, safe products. Traceability helps organizations comply with industry-specific regulations, avoiding fines, penalties, and legal liabilities.
- Supply Chain Optimization: Traceability enables better visibility and understanding of supply chain dynamics. This, in turn, facilitates informed decision-making, minimizes waste, and improves overall supply chain efficiency.
- Continuous Improvement: By analyzing data collected through traceability systems, businesses can identify opportunities for optimization and innovation. This leads to continuous improvement in products, processes, and overall operations.
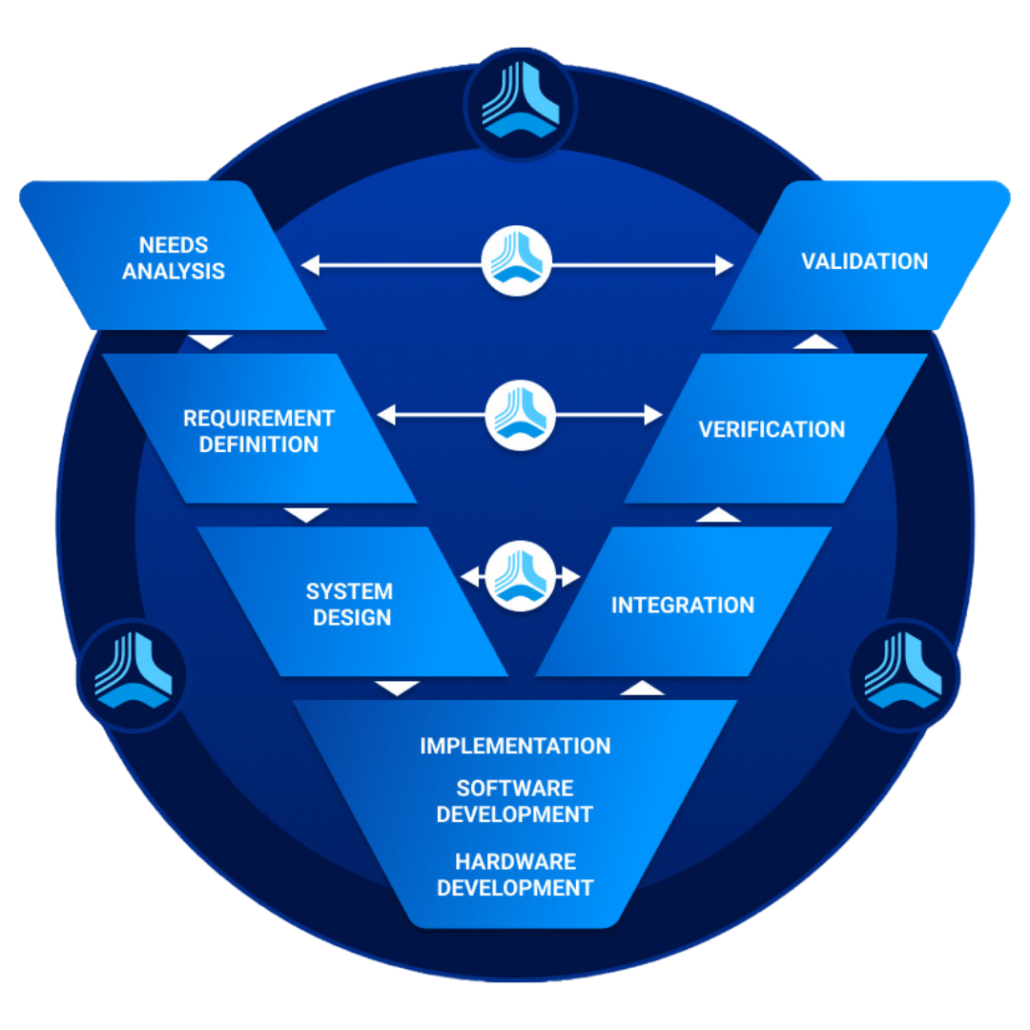
What is Requirements Traceability? Connecting the Dots
Requirements traceability is the practice of linking product, software, or system requirements to design, development, testing, and final delivery. This process ensures that every stage of the product’s lifecycle aligns with the initial set of requirements. By establishing a clear traceability path, organizations can enhance product quality, reduce defects, and mitigate the risk of project failure. However, challenges arise when managing complex projects with numerous interdependencies, making it challenging to maintain clear and comprehensive traceability matrices. Employing advanced project management and requirement tracking tools can aid in addressing these challenges effectively.
Three Key Traceability Challenges
1: Compliance Traceability: Navigating the Regulatory Maze
Compliance traceability refers to the ability of an organization to track and document the complete history of a product or process to ensure conformity with applicable regulations. Different industries have specific compliance requirements – such as ISO 26262 for automotive and ISO 14971 for medical devices – that must be met to ensure consumer safety and to protect public health. Maintaining compliance can be challenging due to the complexity of regulations, which often vary between countries and are updated from time to time. As a result, businesses must invest significant effort in establishing comprehensive traceability measures to stay ahead of evolving compliance standards. Without proper traceability, organizations face failed audits, delays to market, and loss of market share.
2: Lot Traceability: Unraveling Product Journey
Lot traceability involves the tracking of individual batches or lots of products from the point of origin to the end consumer. In industries like pharmaceuticals and electronics, where product recalls can have serious consequences, lot traceability is vital for identifying and addressing issues swiftly and accurately. The challenge lies in accurately capturing and managing data throughout the product’s lifecycle, especially in industries with complex supply chains. Implementing advanced labeling and data management systems can help overcome these hurdles, ensuring the ability to trace the exact journey of each product lot.
3: Traceability Platform: The Need for Interoperability
A traceability platform is a centralized system that captures and consolidates data from various stages of the supply chain or production process. Developing a unified traceability platform is essential for streamlining data collection, analysis, and reporting. However, one of the significant challenges is achieving interoperability between different stakeholders, such as design teams, engineering, quality assurance, suppliers, and manufacturers. Integration issues, data format discrepancies, and data security concerns can hinder the seamless exchange of information, making it critical for organizations to work towards standardized data formats and secure communication protocols.
RELATED ARTICLE: Requirements Traceability Benchmark
How to Improve Traceability for Better Accountability and Efficiency
Traceability Score™ – An Empirical Way to Reduce the Risk of Late Requirements:
Late requirements are a well-known risk to product development – however, there has never been an empirical method to mitigate the risk of late requirements and the burden they put on project teams – until now.
Read this research study to learn more about how, using our proprietary database of metadata from over 50,000 complex product development projects, Jama Software® is the first to:
- Define late requirements
- Measure the burden that late requirements add to product development projects
- Identify managerial practices that empirically reduce the risk of late requirements
- Show how measuring and monitoring the Traceability Score of projects helps resolve issues early and mitigate development risk.
Live Traceability™ in Jama Connect®
Implementing a traceability system manually is very challenging, using a modern requirements management and traceability platform like Jama Connect® automatically creates Live Traceability ™ throughout the development process. With Jama Connect, engineering organizations can intelligently manage the development process by leveraging Live Traceability across best-of-breed tools to measurably improve outcomes.
Conclusion
Traceability is an indispensable aspect of modern businesses, offering numerous benefits ranging from enhanced quality control to regulatory compliance. While implementing effective traceability systems comes with its share of challenges, organizations that prioritize traceability and invest in robust solutions will be better equipped to thrive in a competitive and rapidly changing marketplace. Embracing traceability not only ensures accountability and efficiency but also demonstrates a commitment to the well-being of consumers and the overall success of the enterprise.
Note: This article was drafted with the aid of AI. Additional content, edits for accuracy, and industry expertise by Gary Hayes, Decoteau Wilkerson, and McKenzie Jonsson.
See Jama Connect’s Live Traceability™ in action in this demonstration
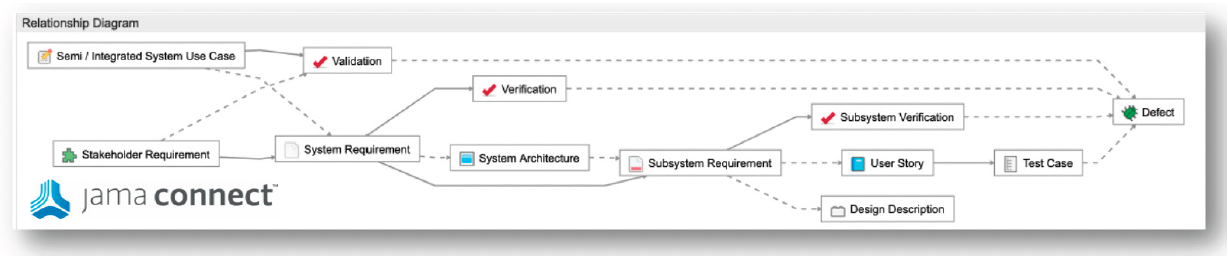
Traceability refers to the relationships between items showing evidence of requirement decomposition and verification coverage.
Book a Demo
See Jama Connect in Action!
Our Jama Connect experts are ready to guide you through a personalized demo, answer your questions, and show you how Jama Connect can help you identify risks, improve cross-team collaboration, and drive faster time to market.