Traceable MBSE™ in Action: Integrating Sparx Enterprise Architect with Jama Connect®
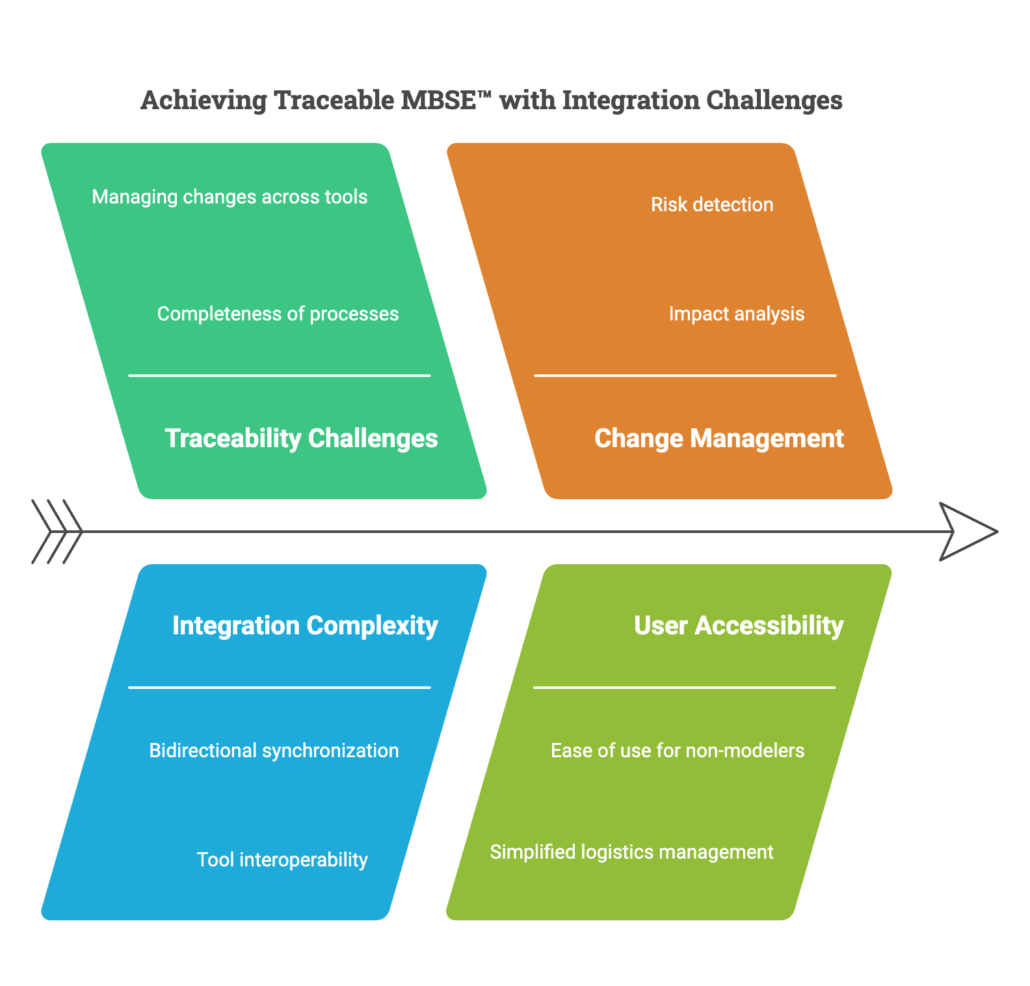
In the complex systems engineering landscape, maintaining Model-Based Systems Engineering (MBSE) across requirements and architecture is a major challenge. Engineers must ensure that high-level requirements flow seamlessly into architectural elements while managing changes across multiple tools.
With the integration between Sparx Enterprise Architect and Jama Connect®, teams can achieve Traceable MBSE™ with bidirectional synchronization of requirements, architecture elements, and diagrams. This enables a holistic view of system design, ensuring real-time traceability, impact analysis, and compliance with predefined processes.
In this blog, Atef Ghribi, Senior Solutions Architect at Jama Software, demonstrates the Sparx Enterprise Architecture integration with Jama Connect.
TRANSCRIPT
Atef Ghribi: Hello. My name is Atef Ghribi, and I’m a Senior Solutions Architect at Jama Software. Today, we will be walking through the Sparx Enterprise Architect integration. But before looking at the tools in action, let’s explore the goal we are trying to achieve as well as the following approach.
Some of the major questions that systems engineers are faced with are related to traceability and how to ensure its completeness based on predefined processes, methodologies, and rules. Making sure that there are no gaps in the process and that all the needs and high-level requirements are covered and satisfied by the lower-level requirements as well as architectural elements, and figuring out how to overcome the challenges of managing changes across the traceability chain, which in most of the cases spans over and across multiple tools. Applying that to the architecture context results in questions like, how do architecture changes impact requirements and vice versa?
As MBSE leaders and advocates, the question is how to make sure that MBSE is accessible and usable easily and efficiently to non-modelers without the need to take care of all the logistics and know what the architecture tools require. With integrations to architecture tools, including Enterprise Architect, Jama Connect enables its users to leverage traceable MBSE to work and interact with the architecture providing a holistic overview of the whole systems engineering process.
Traceable MBSE is a technical approach for the creation, consumption, and measurement of systems engineering data with Jama Connect frameworks for achieving Live Traceability™. The way it works is by enabling bidirectional synchronization of requirements and architecture elements between Jama Connect and Enterprise Architect, as well as syncing diagrams and traceability from Enterprise Architect to Jama Connect as the central engineering management repository.
Jama Connect uses the data to enable intelligent engineering management, providing the ability to detect process risks and identify gaps, measure progress and coverage, and analyze the impact of changes. What we will see in the integration is a simple flow between requirements and architecture elements, starting by creating requirements within Jama Connect and transitioning to Enterprise Architect to start using those requirements in the architecture, where we will be creating architectural elements like blocks, allocating the new requirements to them by creating dependency traces. And that’s all we will need to do as users. The integration will then take care of syncing those changes from the architecture back to our central engineering data repository, Jama Connect. Let’s see this in action.
RELATED: Traceable MBSE™ in Jama Connect: Quickstart Guide
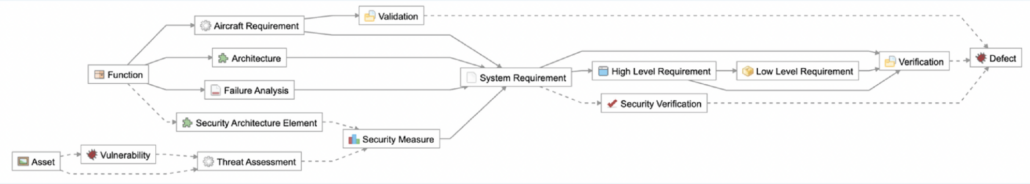
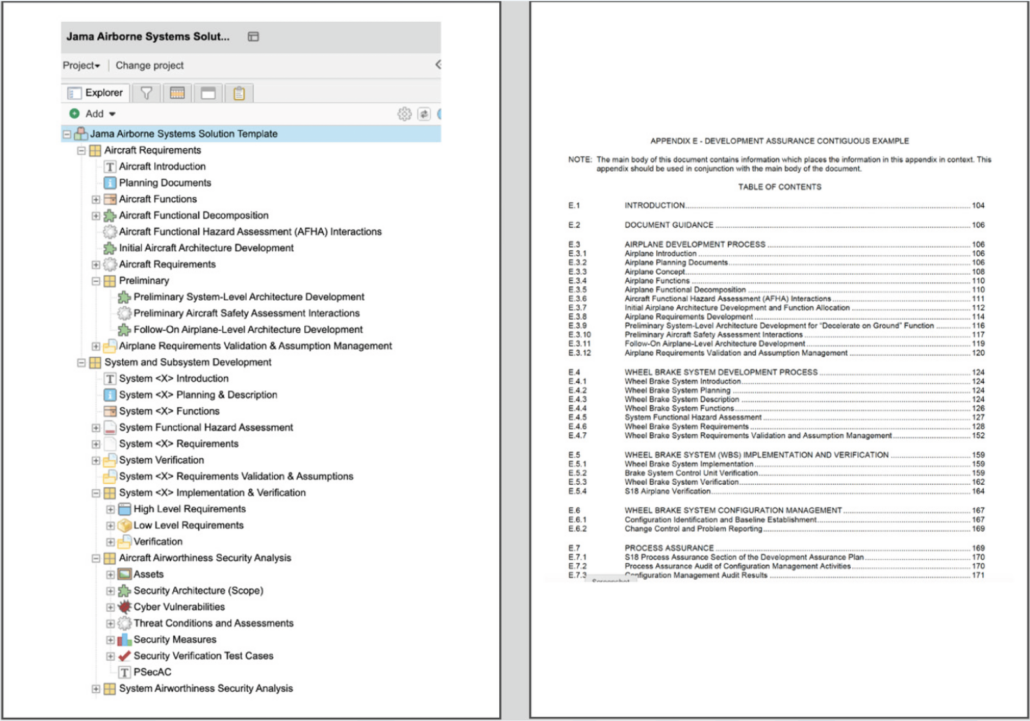
Ghribi: What we see right now in front of us is the Jama Connect project that we are using for the integration, governed by this process or the so-called relationship rule diagram, where we can see the relationship rules that are defined and expected for this project. This will be the instrument that helps us measure the progress and coverage and identify the gaps later. What is interesting for us in the context of this integration are the two item types, system requirements, and architectural elements, as well as the relationship between them that enables users to allocate system requirements to architectural elements.
If we look at the left-hand side of the screen, we can see our project tree, which is the place where we store the content of our project. And we can there also find the system requirements that are managed within this project. So here as a system requirements engineer, I’m gonna be able to create a new system requirement that will be synchronized based on the integration to our Enterprise Architect. So keeping things simple, I’m gonna call this new system requirements.
We can select a type, and we can give it some text as a description. Let’s say description text. And we can save this one to our Jama Connect database.
The integration works now in the background to ensure a real-time synchronization of these changes into our respective EA project. If we also look at another location inside of our project, we can see the place where we defined the integration to sync our architectural elements. Both the diagrams as well as the architectural elements will be synchronized here. We will get back to this later to see how we change or how the changes that we’re gonna do in Enterprise Architect will be updated here.
Let’s switch now to Enterprise Architect and explore the project structure and see if we can find that new system requirement that we just created in Jama Connect. We are keeping the structure of this project simple. And for the sake of simplicity also, as you can see inside of the folder of requirements, we just have a plain list of our system requirements without any folders or any informational elements.
And as we can see, we can find the new system requirement that we just created listed here. So as an architect, I can now use that new input and go to my architecture and create a new architectural element. Save and close. That should create our new item in the Explorer for the project. Now we can start using that new element in our diagram, and you will be able to just place it inside of the diagram and link it. We can do the same for our requirement to create the traceability and allocate that requirement that we just got into the new architectural elements.
And just by creating the relationship as a dependency, we can make sure that now we have the traceability from our system requirements into our architectural element. We can now save the changes in this diagram. As an additional step, I will go to our requirements and start making some changes just to synchronize back and see how the description will change if we just add some changes from EA. Saving. And now we can go back to Jama Connect and explore the changes there.
RELATED: Intelligent Engineering Management with Jama Connect Live Trace Explorer™
Ghribi: Now as we go back to Jama Connect, we can explore our architecture again and see if we can see that new system architectural element. Just need to refresh first our trajectory. And now we can see that new element that was just created inside of our Jama Connect database. Now I can also take a look at the diagrams and see that internal block diagram that just got updated by the integration. In addition to these updates inside of my Jama, I can see also the changes that were applied to my requirement. I can start seeing the changes, that were just, synchronized. I can also start comparing, and understanding what exact changes were now made and modified between the different versions of my requirement.
In addition to that, the traceability that we just created inside of Enterprise Architect can also be seen here. If I go and open the live trace view inside of Jama Connect and scroll up to see how my architectural elements are synchronized and traced to system requirements, I can see the relationship between the new system requirements and the architectural element that was created inside of Enterprise Architect, also inside of charmer.
What we can also see in this view are all the gaps related to all the architectural elements that do not have any system requirements allocation. We can see the same information from the system requirements perspective, this time covering more system requirements. So if we just narrow down our trace view to our system requirements on the left-hand side of the screen and to our architectural elements on the right-hand side of the screen, we can start also seeing all those other system requirements that do not have any coverage or allocation into architectural elements based on the predefined process assigned to this project. We can see the same information also in our dashboard.
So if we use filters and widgets, we can simply see that information in real time and be able to capture any gaps in the process before it’s too late. Now Jama Connect helps us also to get a holistic overview of our project just by using the Live Trace Explorer™ I can just expand here on my project and open a full coverage view that compares the project or the state of my project to the process assigned to it and defines and shows a trace score in real time where I can focus on the exact KPIs and metrics that are relevant for me. For our case today, the architectural elements cover our system requirements where we can trust the progress and see the covered percentage in real time.
As soon as anything changes within Jama Connect or in Enterprise Architect, these values will be updated in real-time, and we can keep track of the progress. Thank you for watching this session on the Enterprise Architect integration for Jama Connect. If you are an existing customer and want to learn more, please reach out to your customer success manager or consultant.
If you would like to learn more about how Jama Connect can optimize your product development process, please visit our website at jamasoftware.com. If you are already a Jama Connect customer and would like more information about release management via reuse and synchronization, please contact your Customer Success Manager or Jama Software Consultant.








![[Webinar Recap] Transform Engineering Processes: Bridge Gaps Between Teams and Tools Effectively [Webinar Recap] Transform Engineering Processes: Bridge Gaps Between Teams and Tools Effectively](https://www.jamasoftware.com/media/2025/01/Transform-Engineering-Processes.png)