In this blog, we recap our recent whitepaper, “Leveraging Jama Connect and Jira for Enhanced Requirements Management” – Click HERE to download it in its entirety.
Leveraging Jama Connect and Jira for Enhanced Requirements
Think you can manage your complex software requirements with Word and Jira alone? Think again.
In software development, teams need tools that enable them to manage requirements, ensure traceability, and adapt to changes without losing sight of their goals. Many companies rely solely on Atlassian Jira, often paired with Word or Excel, to handle requirements and track development tasks.
While Jira is highly effective for tracking implementation progress, it lacks essential features for managing requirements throughout the entire development lifecycle.
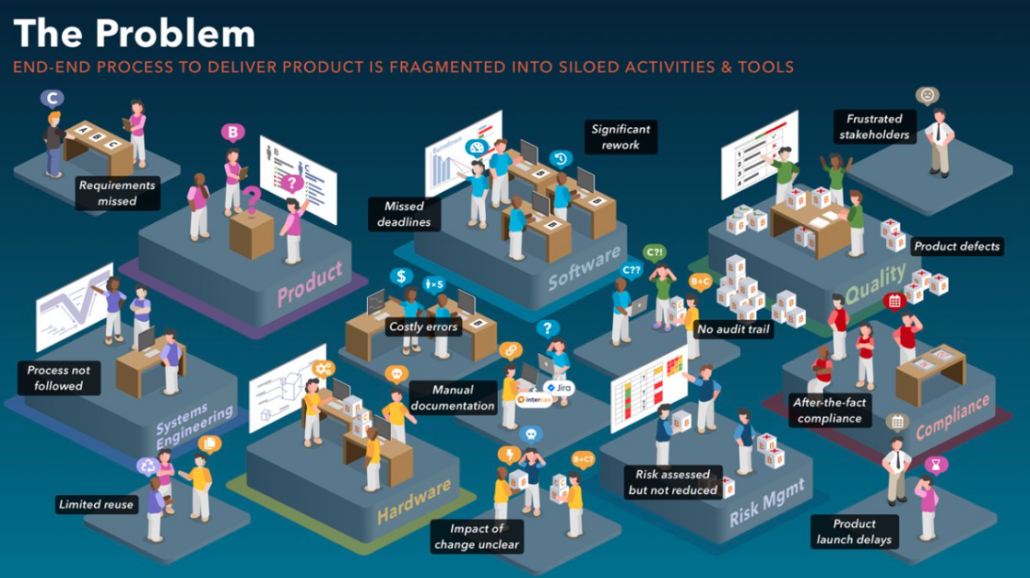
The limitations of using Jira alone can lead to costly setbacks, such as rework, missed deadlines, delayed rollouts, and compromised quality. These challenges stem from a lack of traceability, inefficient review processes, limited project visibility, and an incomplete definition of the system.
This eBook explores these issues and introduces a solution: integrating Jama Connect with Jira. Jama Connect enhances requirements management, enables Live Traceability™, streamlines reviews, and provides real-time insight into development progress.
Together, Jama Connect and Jira empower teams to achieve better software development outcomes
1. The Limitations of Using Jira Alone for Requirements Management
Lack of Traceability
The challenge of managing requirements with flat or disparate files like Word or Excel is significant. Teams that use these tools alongside Jira often struggle to keep requirements aligned with development tasks. Manual traceability in these formats is resource-intensive, prone to errors, and leaves significant gaps in coverage.
Without proper traceability, teams have limited visibility into their project’s true status, which can lead to costly rework and project delays. In fact, lack of traceability is one of the leading causes of negative project outcomes. When you can’t see how requirements connect to development and testing, the project suffers, and costs escalate — especially if defects are discovered later in the lifecycle. According to research done by INCOSE, the cost of fixing a defect can be up to 110 times more expensive if it’s found during validation rather than early on.
Jama Connect’s Live Traceability solves this problem by creating a digital thread through every level of development, from customer needs to verification and validation. This digital thread ensures that all requirements are covered and connected to development tasks, giving teams confidence that they’re meeting their goals and satisfying customer needs. Later in this paper, we’ll explore the many ways Live Traceability can dramatically improve your development process.

RELATED: Traceable Agile™ – Speed AND Quality Are Possible for Software Factories in Safety-critical Industries
Inefficient Requirement Reviews
Reviewing requirements using Word documents can be frustrating and inefficient. A business requirements document often contains hundreds or even thousands of requirements. Teams must wait for the entire document to reach a draft state before circulating it for feedback. Stakeholders then provide comments through a combination of Word’s review features and emails, creating a fragmented and time-consuming process.
In this scenario, the burden falls on the business analyst to compile feedback, chase down reviewers, and manage multiple rounds of review cycles. This process is not only inefficient but also risks missed feedback or inconsistencies, as it’s difficult to track changes from one review cycle to the next.
Jama Connect’s Review Center streamlines this process. It allows teams to break down reviews into manageable parts and send specific sections out for feedback. Instead of waiting for an entire document to be finalized, teams can initiate reviews iteratively. The Review Center also automatically creates a baseline at the start of each review, providing a clear record of the requirements’ state before any feedback or changes are made. This reduces review cycles and accelerates consensus, saving valuable time and resources.
Business Analysts and Stakeholders are Frustrated
The lack of an end-to-end tool connecting stakeholders, business analysts, and software development teams is a major gap. Traceable Agile™ in Jama Connect is the answer. With Traceable Agile, there is no change for software teams and the development process is supported for both business analysts and stakeholders. Learn more here >>
2. The Value of Creating a Digital Thread with Jama Connect and Jira
Providing Development Insight
Jira is a powerful tool for tracking development tasks, prioritizing work, and managing sprint schedules. However, it lacks comprehensive visibility into whether requirements are actually being met. If development tasks, such as user stories, aren’t directly linked to requirements, it’s impossible to know how close the project is to meeting customer needs.
Unlinked development tasks open risks like scope creep, rogue development, or unintentional changes that affect other parts of the system. In these cases, teams may spend time on tasks that aren’t aligned with the project’s core requirements, leading to wasted resources and delayed timelines.
By integrating Jama Connect with Jira, teams can bridge this gap. Jama Connect retains the requirements context, while Jira provides insight into development progress. Each team can work within its tool of choice while sharing critical information, such as real-time updates on task status. This integration enables project managers to see how development is progressing against requirements, ensuring that every task is necessary, and every requirement is covered.
Only Jama Connect Delivers a Digital Thread that is Measurable and Live Traceable Across Best-of-Breed Tools Jama Connect’s digital thread connects best-of-breed tools like Jira and Cameo and enables you to auto detect risk early across all engineering disciplines. This has been shown to enable proven improvement to the product development process.
Clear Definition of System Requirements
A common misconception about Agile is that formal requirements documentation is unnecessary. Some teams try to decompose customer needs into user stories in Jira, thinking that’s sufficient. However, this approach has limitations. User stories describe specific interactions or functions from a user’s perspective, but they don’t provide the comprehensive requirements needed for a full system definition.
Traceable Agile ensures that every requirement and feature is documented, versioned, and kept up to date, providing a clear, evolving definition of the system. Unlike user stories, requirements offer a functional description of what the system must do, ensuring alignment with customer needs. With Jama Connect, you get a single source of truth for the system, one that evolves over time and reflects the current state of requirements, while also keeping a record of every change that’s made.
RELATED: Buyer’s Guide: Selecting a Requirements Management and Traceability Solution
Companies Choose Agile for Speed, Jama Connect Delivers Speed AND Quality
Jama Connect solves common challenges with Agile initiatives, such as maintaining standards compliance, coordinating hardware and software teams, managing defects, reducing rework, and ensuring customer quality. Traceable Agile speeds the flow of software and hardware development and maintains the current and historical state of development quality to auto-detect issues early. Watch the demo >>