This post was originally published on January 7, 2022.
Requirements Traceability – How to Go Live
Requirements traceability is required by many industry standards to ensure product quality and safety. The industry standards are based on decades of progress made in systems and quality engineering research with requirements traceability at the core. Benefits from requirements traceability are achieved if and only if traceability is used as a tool during the product development process. These benefits include greatly reduced or eliminated delays, defects, cost overruns, and rework. Here is an overview of the best practice approach to achieve Live Traceability™.
Live Traceability vs. After-the-fact Traceability
Let’s start with some definitions to make sure we are all on the same page. Requirement traceability is defined as tracking the development progress of product requirements from definition and design through development, testing, verification, and validation. There are two forms of requirement traceability: after-the-fact traceability and Live Traceability.
- After-the-fact traceability occurs after the product has been developed and is typically a highly manual effort to try and re-create artifacts to demonstrate traceability that should have occurred during the development process but did not. This effort is undertaken solely for complying with industry standards and satisfying auditor requests for demonstration of process maturity.
- Live Traceability occurs in real time as the product development process progresses to improve overall productivity (by ensuring engineers across disciplines are always working off the most recent and correct versions) and to reduce the risk of negative product outcomes (delays, defects, rework, cost overruns, recalls, etc.) through early detection of issues. The benefits of early detection of issues are significant. Research by INCOSE found that issues not found until verification and validation are 40 to 110 times more costly than if found during design. For this reason, most companies want Live Traceability but are stuck with legacy tools and spreadsheets that do not support it. Since each engineering discipline is allowed to choose its own tooling, the result is a large number of tools with no relationship rules or mechanisms to create Live Traceability across them.
RELATED POST: Requirements Management Guide: Requirements Traceability
So how do you achieve Live Traceability?
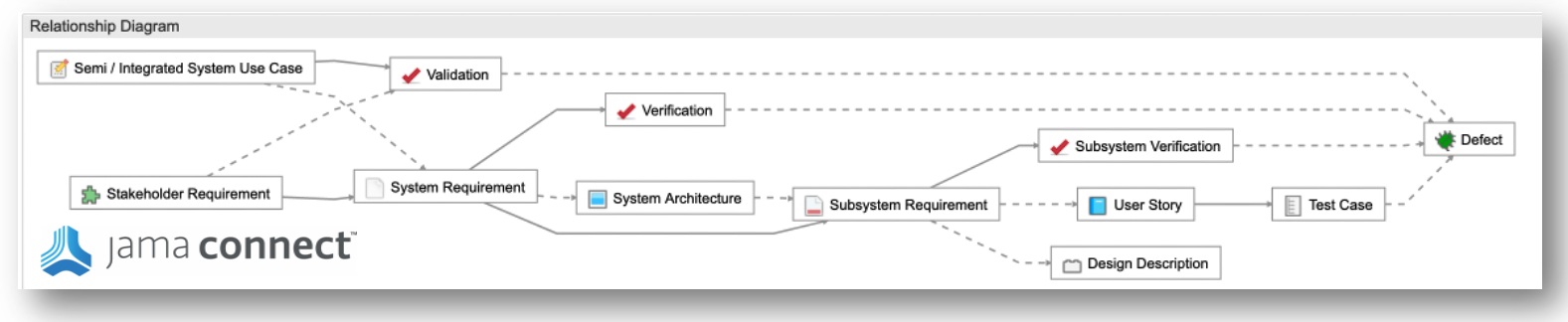
Step 1: Define a Traceability Model
Live Traceability requires a model of the key process elements and their relationship rules to monitor during the development process. The systems engineering V Model is a useful framework to start with for data object and relationship definition. Jama Connect® uniquely provides a point and click, configurable, relationship rule capability to enable Live Traceability. Below you see a sample relationship rule diagram from Jama Connect. Relationship rules vary by industry and company-specific requirements. Best practice templates are provided to comply with industry standards and configured to meet client-specific needs. The definition of a traceability model forms the foundation for model-based systems engineering since it defines model elements and their relationship to each other in a consistent manner across the entire system architecture.
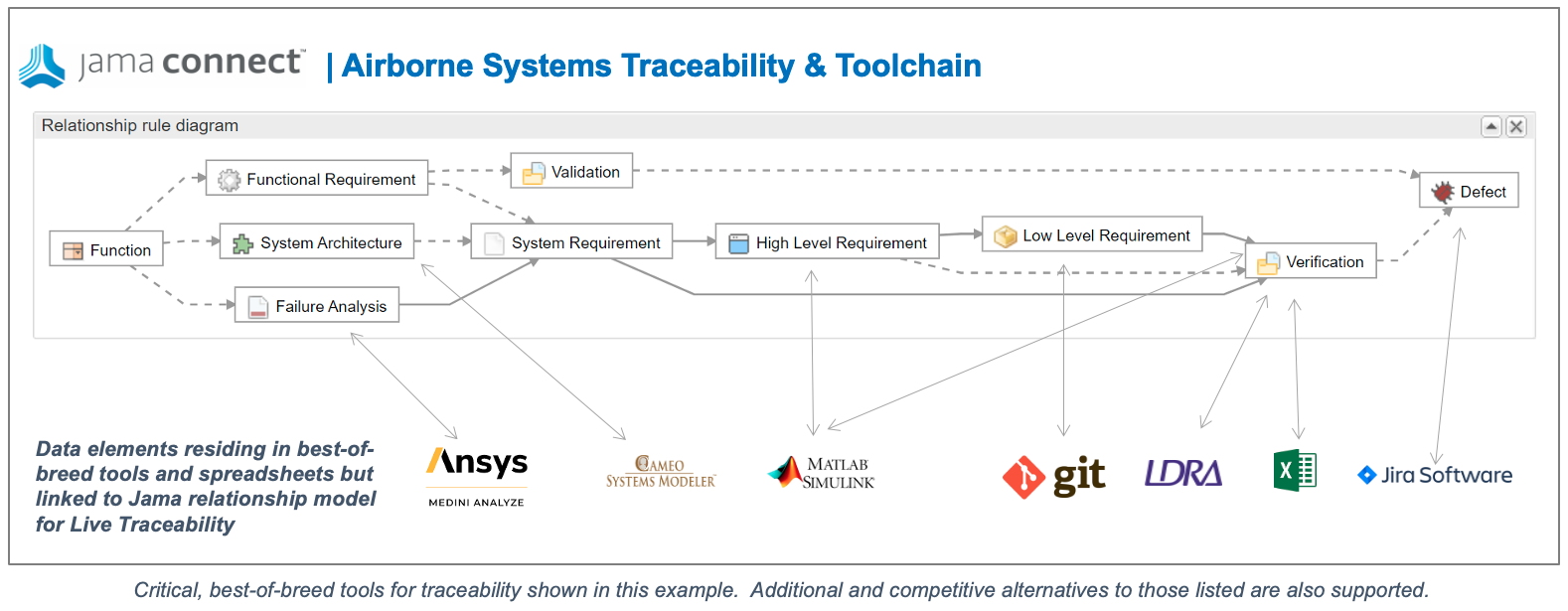
Step 2: Setup Continuous Sync for Siloed Tools/Spreadsheets
Once the relationship rules are defined, the next step is to set up continuous sync with best-of-breed tools and spreadsheets used by the various engineering disciplines. The traceability diagram below shows a typical example of best-of-breed tools and where they sync in the Jama Connect relationship model to deliver Live Traceability.
Most companies prioritize the areas of the traceability model that are most prone to lead to costly issues in the absence of a continuous sync. Most commonly, these areas are:
- Software task management – directly linking the decomposition of requirements into user stories enables Live Traceability through the software development process through testing and defect management. The most common best-of-breed tools used are Jira and Azure Dev Ops.
- Test automation – test cases are managed in Jama Connect to align to requirements and ensure traceability across all engineering disciplines with the test automation results sync’d to the traceability model at the verification step. The most common test automation tools are TestRail and qTest.
- Risk analysis (DFMEA/FMEA) – is most often conducted in multiple Microsoft Excel spreadsheets and the assumption has been that Live Traceability was not possible with Excel. Jama Connect is the first requirements management solution to enable Live Traceability with Excel functions and spreadsheets. Risk teams can now work in their preferred spreadsheets AND for the first time achieve live traceability to stay in sync with changes made by any engineering team. Ansys Medini is also a supported integration.
- Model-based systems engineering (MBSE) – the first step in MBSE is to define a relationship model between all product requirements. Once a relationship model is defined, then specifications can be determined through modeling. Jama Connect uniquely provides model-based requirements to sync logically with a SysML modeling tool like Cameo No Magic. Other requirements management tools do not ensure a model-based approach, which most often leads to inconsistent and conflicting fields across teams and projects and provides no coherent relationship model.
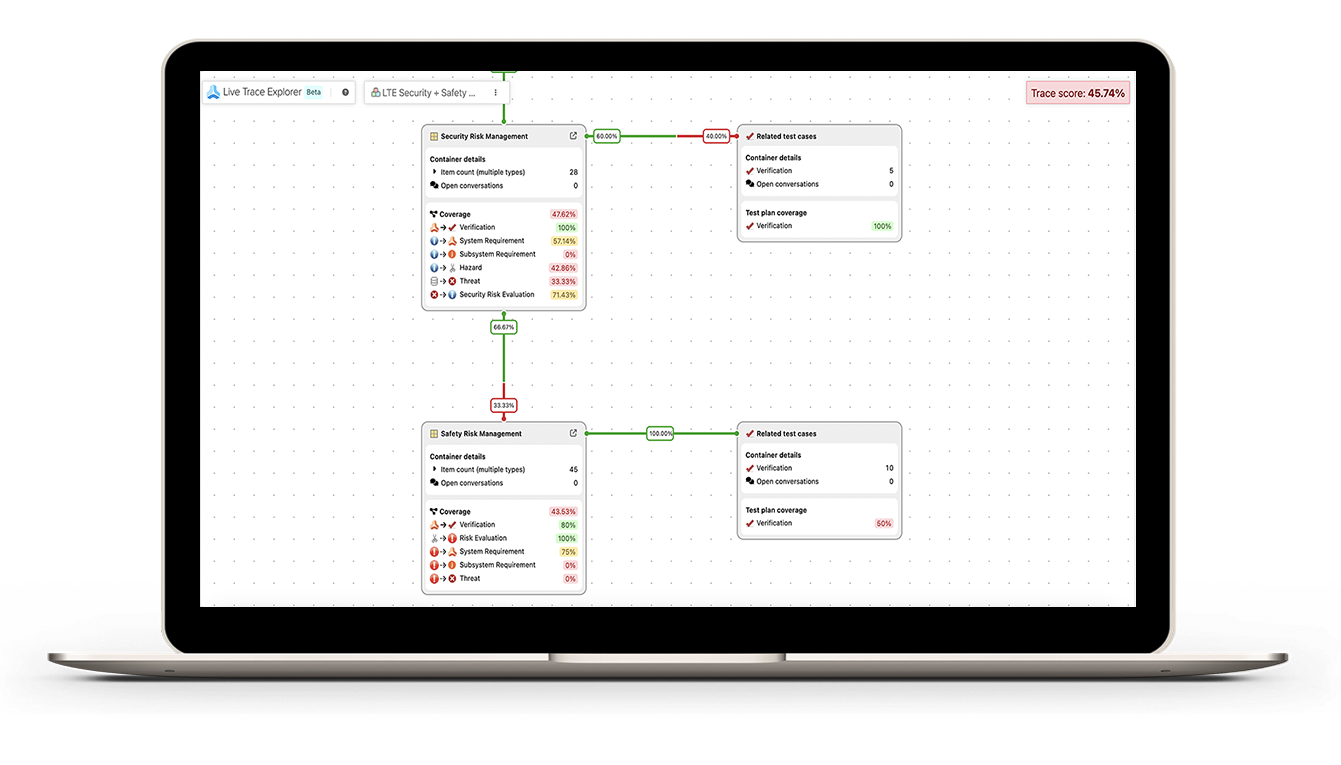
Step 3: Monitor for Exceptions
Live Traceability provides the ability, for the first time, to manage by exception the end-to-end product development process across all engineering disciplines. The traceability model defines expected process behavior that can be compared to actual activity to generate exceptions. These exceptions are the early warning indicators of issues that most often lead to delays, cost overruns, rework, defects, and recalls. Below is a view of our Live Trace Explorer that shows you the LIVE state of development for any level of the development project you choose – from the entire cross-discipline effort down to a specific sub-component. Areas of greatest risk appear in red to show where requirement or verification coverage is lacking. Traceability is now a measurement that can be managed and improved with an overall Traceability Score and coverage and verification percentages..
Benefits of Live Traceability
The main benefits of Live Traceability across best-of-breed tools are as follows:
- Reduce the risk of delays, cost overruns, rework, defects, and recalls with early detection of issues through exception management and save 40 to 110 times the cost of issues identified late in the process.
- Comply with industry standards with no after-the-fact manual effort.
- No disruption to engineering teams that continue working in their chosen best-of-breed tools with no need to change tools, fields, values or processes.
- Increase productivity and satisfaction of engineers with the confidence that they are always working on the latest version, reflective of all changes and comments.
LEARN MORE
- Requirements Traceability – How to Go Live - October 30, 2024
- What is the Definition of a Digital Thread? - September 18, 2024
- Traceable Agile™ – Speed AND Quality Are Possible for Software Factories in Safety-critical Industries - October 3, 2023