This is part 2 of a two-part blog series covering our eBook, “A Complete Guide to Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASIL)“, in which we discuss this important automotive safety standard and how to comply with it. Part 1 can be found HERE and the entire eBook can be downloaded HERE.
A Complete Guide to Automotive Safety Integrity Levels (ASIL) Part 2
What are some examples of ASIL classifications?
Though there is some degree of subjectivity within the different ASIL classifications, some systems and components have fairly consistent classifications. Here are a few examples:
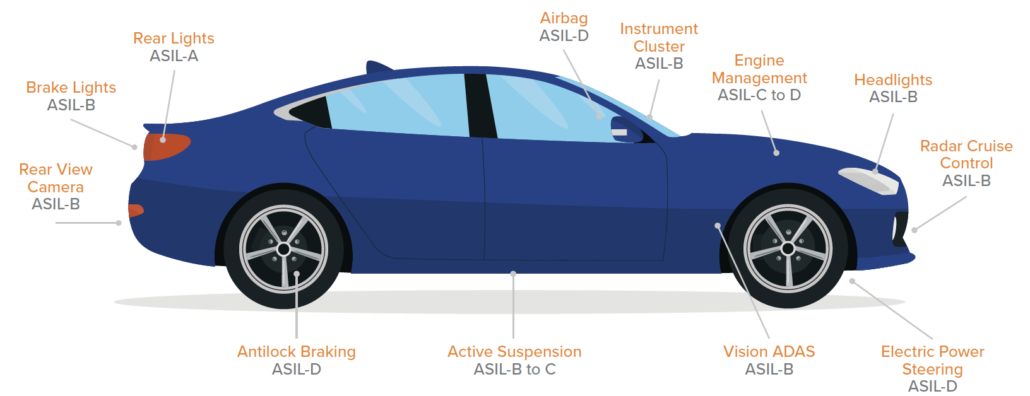
- ASIL D: Airbags, antilock braking, electric power steering
- ASIL C: Adaptive cruise control, battery management, suspension ASIL B: Brake lights, rear view camera, instrument cluster
- ASIL A: Rear lights, heating and cooling, body control units
- QM: GPS/Navigation systems, satellite/digital radio, connectivity (USB, HDMI, Bluetooth)
Even within these examples, there may be variance between different models, manufacturers, or risk assessments. For example, depending on other factors, “Engine management” risks could be ASIL C or D, and various powertrain systems and risks could vary between ASIL B and ASIL D. A host of considerations go into assessing risk and assigning levels.
In addition, it is possible for ASIL to change. For example, an OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) may determine that a component has a level of ASIL B, but once the component is integrated with other systems, the level may be raised or lowered in conjunction with an additional hazard analysis and risk assessment.
Learn more about simplifying validation: Jama Connect Functional Safety Kit for Automotive Development Teams
What are the challenges of ASIL?
Although the chart on page 11 shows how to arrive at an ASIL based on the severity, exposure, and controllability levels, there is some amount of subjectivity involved in assigning those levels. For example, road conditions, environmental factors, traffic density, driver competence, and the likelihood of exposure can all vary widely. A driver who is operating a vehicle on a wide, empty, dry road may be more likely to control for a hazardous event than a driver operating in heavy traffic during a rainstorm. The ASIL classification system depends on subjective interpretation with words such as “usually,” “likely,” and “probably,” which involves some level of educated judgment on the part of engineers and developers.
Another challenge with determining ASIL levels is the temptation to make an assumption based on past level assignments without doing a full hazard analysis and risk assessment. For example, if a system was previously assigned ASIL level B, it might be tempting to assume its current level should be the same. However, improvements in the system or integrations with other systems could change the level. If a GPS system now integrates with camera equipment or some other intelligent technology, that new integration could raise or lower the ASIL level.
Finally, teams that are not keeping good documentation records or tracking requirements properly may arrive at inaccurate ASILs — or even neglect risks entirely. When documentation and requirements aren’t thoroughly tracked, teams may miss key functional safety risks. Requirements tracking and traceability are essential not only for compliance with ISO 26262, but also for the practical market need to thoroughly and accurately assess and mitigate risks.
How does ASIL impact product development?
Once the ASIL for a system has been developed, ISO 26262 defined different levels of rigor that are required based on the ASIL. For example, for ASIL A and B, information notation is sufficient for capturing requirements. This typically means that requirements are written in natural language and augmented with simple figures to illiterate key concepts. For ASIL C and D, a more semi-formal notation is recommended. Requirements are still often written in natural language, but then models of the system are developed to more accurately describe behavior. Developing these models requires additional expertise from the team but increases the accuracy of the documentation and decreases the risk of miscommunication. Teams developing higher ASIL systems often require additional expertise as well as specialized software tools to support the process.
Related: Best Practices to Accelerate Your Automotive Spice (ASPICE) Capabilities
How are ASILs evolving?
The Society for Automotive Engineers (SAE) issued J2980 in 2015 to provide additional guidance for assessing severity, exposure, and controllability. In addition, J2980 itself was updated in 2018, as was ISO 26262.
As automotive technology advances with AI (Artificial Intelligence), self-driving features, and integration to external systems through IoT (internet of things), the concept of controllability presents particular challenges. Currently, “controllability” largely refers to the human vehicle operator, but as automobiles become more able to react independently, the standards for assessing controllability may change. With features that compensate more and more for driver error, cars are becoming safer and more intelligent, decreasing the likelihood of hazards that cause severe injury or death. At the same time, however, access to external systems can introduce cyber vulnerabilities that complicate ASIL considerations.
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities can lead to safety considerations just like hardware failures. As a result, teams are now starting to analyze the safety and security of systems together. ISO 21434 especially makes recommendations that tie in with ISO 26262 to support this process.
Conclusion
One important key to risk assessment and mitigation is unified requirements and live requirements traceability across the entire systems development lifecycle. This underpins industry standards to ensure higher quality, faster cycle times, and less costly rework. Teams can’t be expected to control for risk and document efforts without tracking and managing requirements with Live Traceability™. With increasingly dispersed and cross-functional workforces, creating a single source for all requirements tracking can be key to meeting safety and market needs.
Jama Connect® for Automotive is designed to give automotive development teams the framework they need to meet market demands quickly and efficiently without breaking the bank. Tightly aligned to automotive industry standards and regulations, Jama Connect® simplifies functional safety and improves development cycles across a complex supplier ecosystem.
Whether your team is young or seasoned, small or large, all together or scattered across geographies, Jama Connect for Automotive can help improve processes, reduce costs, improve time to market, and help achieve compliance. To learn more about Jama Connect for Automotive, read our Jama Connect for Automotive Datasheet.
Jama Connect®:
- Provides known processes and practices to those companies that may not have the time to start from scratch and would prefer to leverage something with a proven track record.
- Produces documentation necessary to accurately assess risks for ASIL levels and prove compliance with ISO 26262.
- Gives a central source of information to help break down siloes and improve communication and collaboration between teams.
- Includes consulting services to help you customize your documentation to your company’s
To read the entire eBook, download it HERE
- 9 Strategies To Overcome Challenges In The EU Medical Device Market In 2025 And Beyond - February 6, 2025
- Leveraging Jama Connect® and Jira for Enhanced Requirements - January 30, 2025
- With Hacks on the Rise, Manufacturers Hone Their Cybersecurity Smarts - January 23, 2025